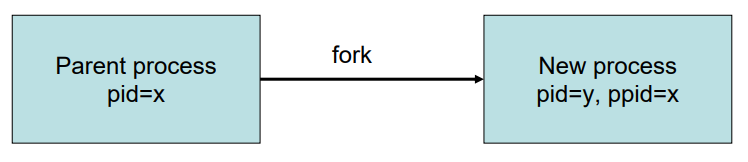建立进程(Process)
在Linux中,创造新进程的方法只有一个,就是函式fork()。其他一些函式,如system(),看起來似乎也能创建新的进程,如果看一下它们的來源码(source code)就会明白,它们实际上也在内部呼叫了fork。包括我们在命令行下运行应用程式,新的进程也是由shell呼叫函式fork制造出來的。
fork
fork是UNIX一个系统呼叫(system call),process fork时,会复制一个跟自己完全一模一样的process (with differentpid),并利用系统呼叫完成之传回值,來区分parentprocess 与child process,而分别赋予child process不同的功能。
fork (.c)
- “fork”的意思就是一分为二,把当前进程复制出一个新的进程。当前的进程就是新进程的父进程,新进程称为子进程。
- fork把子进程ID传回给父进程,把0传回给子进程,通过对传回值的检查就可知道当前是父进程还是子进程。
首先建立一个档案 fork_exam.c,输入以下程式码
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
if ((pid = fork()) > 0)
printf("I am the parent, my pid = %u, my child is pid = %u\n", getpid(), pid);
else if (pid == 0)
printf("I am the child, my pid = %u, my parent is pid = %u\n", getpid(), getppid());
else
{
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}接着编译这个档案并且执行他
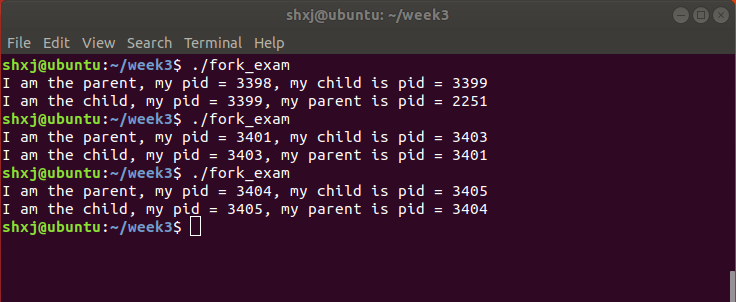
gcc -o fork_exam fork_exam.c
./fork_exam再来将程式码更改成以下,使用视觉化的方式查看进程
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
if ((pid = fork()) > 0){
printf("I am the parent, my pid = %u, my child is pid = %u\n", getpid(), pid);
for (int i=0; i<1000; i++) {
printf("*");
fflush(stdout);
sleep(1);
}
}
else if (pid == 0){
printf("I am the child, my pid = %u, my parent is pid = %u\n", getpid(), getppid());
for (int i=0; i<1000; i++) {
printf("a");
fflush(stdout);
sleep(1);
}
}
else
{
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
return 0;
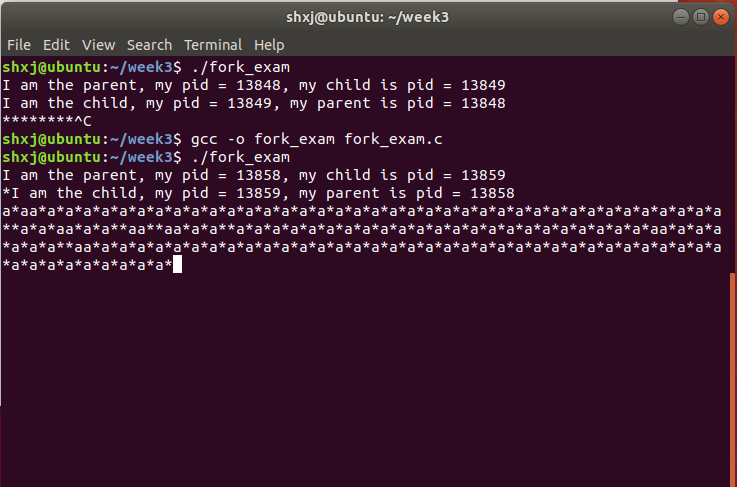
}重新编译一次,再次执行程式
强制中断进程
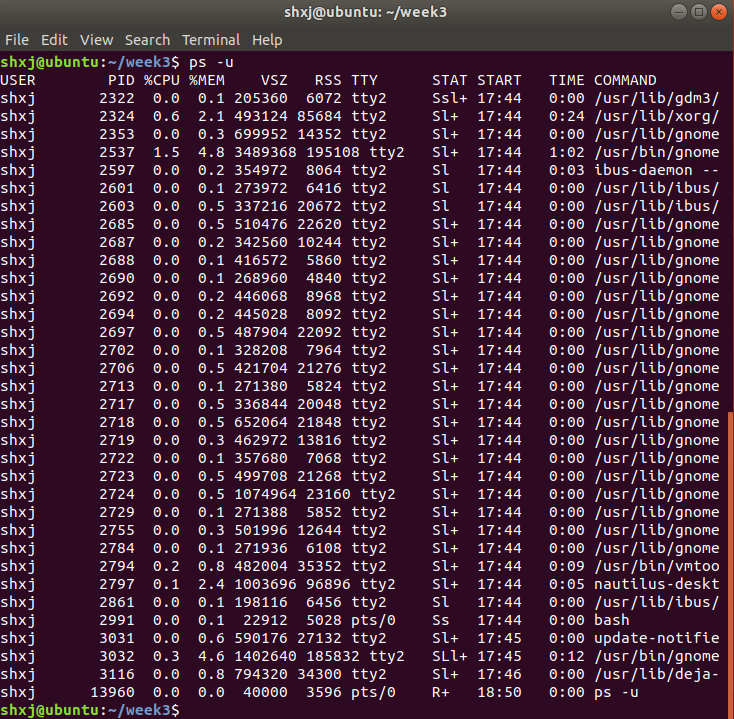
输入以下的指令可以查看目前运行的所有进程
ps -u找到想要中断的进程 pid,使用以下的指令杀掉
kill -9 PIDLatest posts by SHXJ (see all)
- 受保护的内容: NAS 版 Mathbot 管理网站与 Linebot 启动方法 - 2024 年 11 月 15 日
- Realtime 啥鬼的 - 2021 年 6 月 15 日
- nodejs 数学游戏 - 2021 年 6 月 8 日